refer to: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/solidity/solidity_arrays.htm
https://docs.soliditylang.org/en/v0.8.15/types.html#array-members
在Solidity中,array的长度(length) 都是固定的。跟其他静态语言的使用是一样的。
声明
上来就是个固定长度的:
uint myArray[3]
在声明的时候不确定长度:
uint[] myArray;
初始化
下面2个是静态的初始化,作用一样:
uint[] myArray = [1,2,3]
uint[3] myArray = [1,2,3]
下面这个是动态的初始化:
uint size = 10
address[] myAddresses = new address[](size) ;
对数组的赋值 []=
对某个数组的 2+1 个元素赋值,新的值是 c:
myArray[2] = 'c'
可用的变量 length (数组长度), 方法: push(把某个element放到数组中)
uint[] myArray = [1,2,3]
myArray.length ( 3) 见上面
push :
把元素放到数组的最后一位 ,注意:返回啥查询最新的文档
myArray.push(4)
pop
可以把数组的最后一个元素给删掉, 数组长度 - 1 , 返回的内容查询最新的文档, 0.8.15 啥也不返回
myArray.pop()
delete:
把某个元素的值变为 0 (严格的说这不是array的方法)
遍历一个数组
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract TestArray {
event MyLog(int element);
function loopArray(int[] calldata numbers) external {
for(uint i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++ ) {
emit MyLog(numbers[i]);
}
}
}
编译,运行: (记得修改contract address )
// contract 地址要有
const CONTRACT_ADDRESS = "0x5B481532279AbF29ba477cDa324656dc626113F8"
// abi 要有
const contractJson = require('./build/contracts/TestArray.json')
module.exports = async function (callback) {
// web3 是Truffle的自动引入的对象
const contract = new web3.eth.Contract( contractJson.abi, CONTRACT_ADDRESS );
// 获得 network , 这个是根据参数传入的
const network = await web3.eth.net.getNetworkType()
const tx = contract.methods.loopArray([22,33,44])
// 发送!
const receipt = await tx
.send({
from: (await web3.eth.getAccounts())[0],// 使用了HD wallet中的第一个account
gas: await tx.estimateGas(),
})
.on('transactionHash', (txhash) => {
console.log(`Mining transaction ... network: ${network}, tx: ${txhash}`)
})
.on('error', function(error){
console.error(`An error happened: ${error}`)
callback()
})
.then(function(receipt){
console.log('====== events.MyLog: ', receipt.events.MyLog)
callback()
})
}
结果:
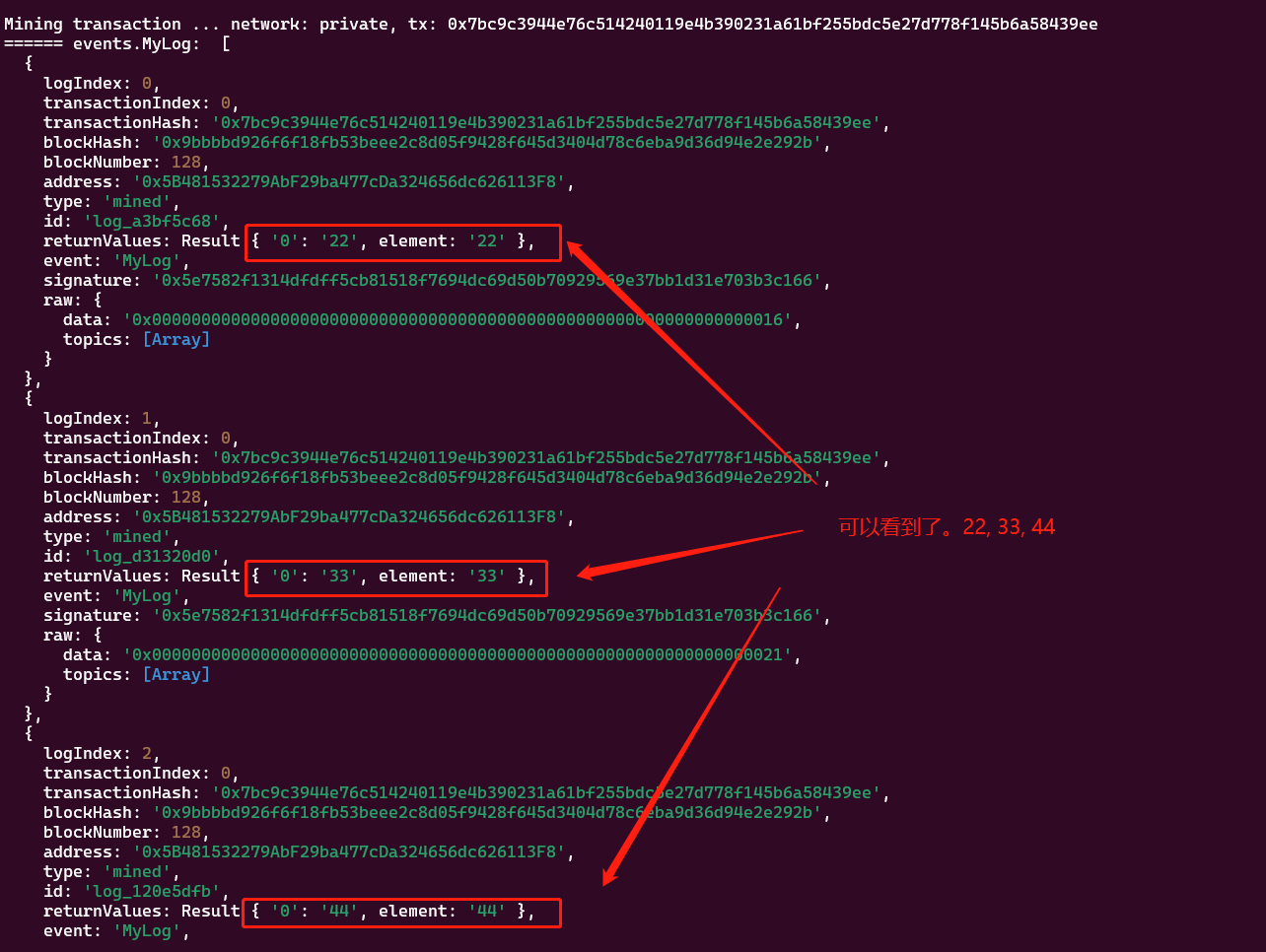
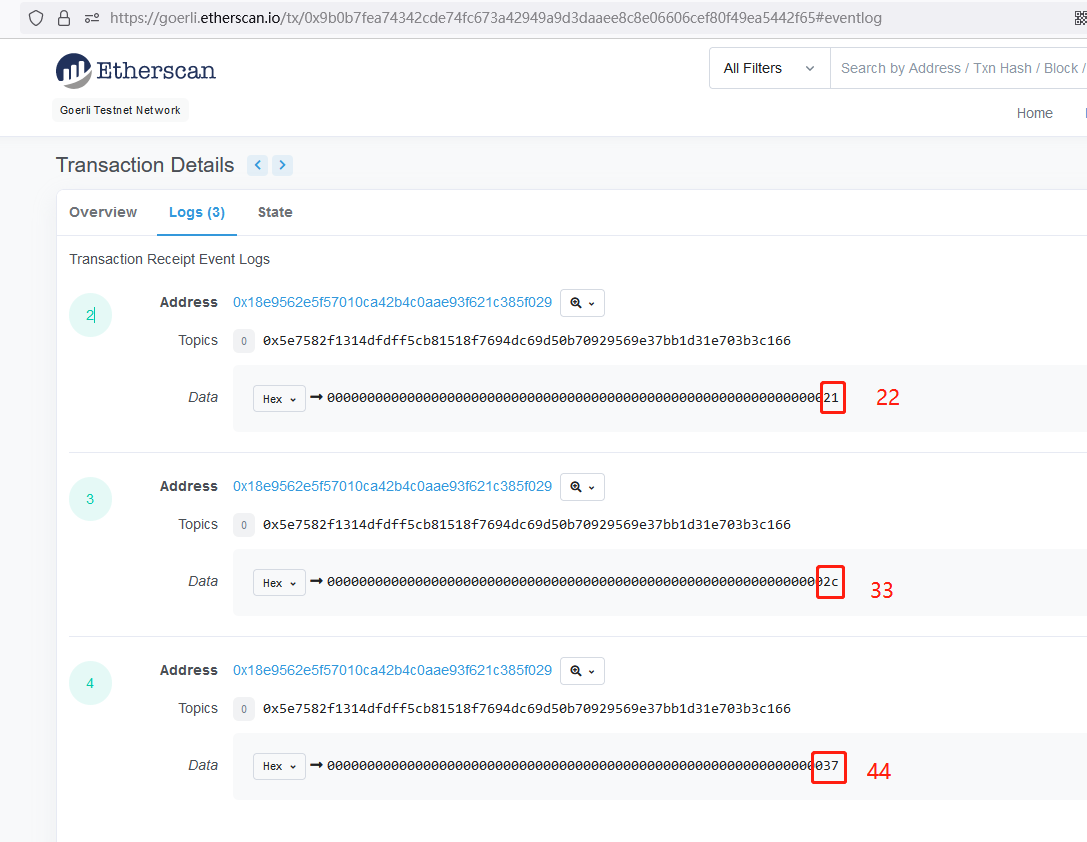
在 etherscan上看也是一样的。
如何删掉某个元素,并且把array的长度减少1, (该数组的顺序会被打乱)
uint[] internal array;
// Move the last element to the deleted spot.
// Remove the last element.
function _burn(uint index) internal {
require(index < array.length);
array[index] = array[array.length-1];
array.pop();
}